Getting Started with Azure Active Directory
Azure Active Directory (AD) is a cloud-based identity and access management service that helps organizations manage users, groups, and applications. With Azure AD, you can control access to your applications and resources, enforce multi-factor authentication, and integrate with external identity providers. In this blog, we will discuss the features and benefits of Azure AD and provide a comprehensive example of how to use Azure AD to manage users and access to applications.
Azure Active Directory (AD) Features and Benefits
Centralized User Management:
With Azure Active Directory (AD), you can manage user accounts and permissions from a centralized location. You can create and manage user accounts, assign roles and permissions, and enforce security policies. This eliminates the need to manage users separately for each application and simplifies the user management process.
Single Sign-On (SSO):
Azure Active Directory (AD) provides single sign-on (SSO) capabilities, allowing users to sign in to multiple applications and services with a single set of credentials. This reduces the number of passwords users have to remember and simplifies the authentication process.
Multi-Factor Authentication:
Azure Active Directory (AD) supports multi-factor authentication (MFA), which adds an extra layer of security to user sign-ins. With MFA, users must provide two or more authentication factors to access an application or resource, such as a password and a verification code sent to their phone.
External Identity Providers:
Azure Active Directory (AD) can be integrated with external identity providers, such as social media accounts or other corporate directories, to provide a unified authentication experience. This allows users to use their existing credentials to access your applications and resources.
Application Management:
Azure AD provides application management capabilities, allowing you to manage access to your applications and resources. You can assign users and groups to applications, enforce security policies, and monitor usage.
Reporting and Analytics:
Azure AD provides reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing you to monitor user activity and access to your applications and resources. You can view reports on user activity, sign-in activity, and more to help you identify potential security issues.
Deploy and manage Azure resources
Example: Managing Users and Access to Applications with Azure AD
To illustrate how Azure AD can be used to manage users and access to applications, let’s consider an example. Suppose we have a small business with 50 employees and three applications: a CRM system, a document management system, and a payroll system. We want to use Azure AD to manage user accounts and access to these applications.
Step 1: Set up Azure AD
The first step is to set up Azure AD. We create an Azure AD tenant and add our users to the directory. We can create users one at a time or use Azure AD Connect to synchronize our on-premises Active Directory with Azure AD.
Step 2: Configure Applications
Next, we need to configure our applications to use Azure AD for authentication. We can do this by registering each application in Azure AD and configuring the appropriate authentication settings.
Step 3: Assign Users to Applications
Once our applications are configured, we can assign users and groups to each application. We can assign users and groups to applications individually or create application groups and assign them to applications.
Step 4: Enforce Security Policies
We can enforce security policies for each application, such as requiring multi-factor authentication or blocking access from specific locations. We can also set up conditional access policies to control access to applications based on user and device conditions.
Step 5: Monitor Usage and Activity
Finally, we can use Azure AD’s reporting and analytics capabilities to monitor user activity and access to our applications. We can view reports on user activity, sign-in activity, and more to help us identify potential security issues.
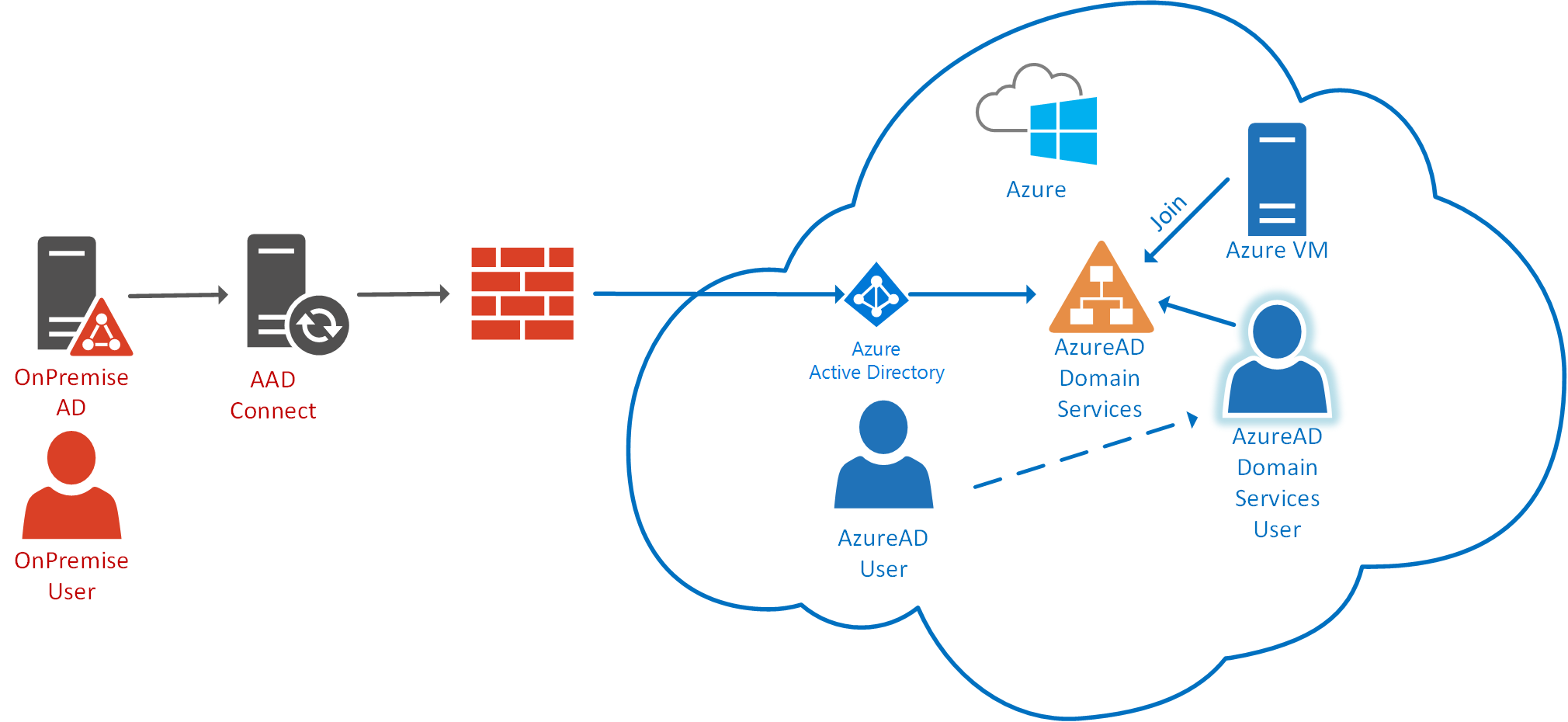
Conclusion
Azure AD is a powerful identity and access management service that can help organizations manage users, groups, and applications in a centralized location. With Azure AD, you can control.