Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud computing has become an increasingly popular way for healthcare organizations to store and manage their data. By storing data in the cloud, healthcare organizations can enjoy a range of benefits, such as increased scalability and reduced costs. However, there are also some potential disadvantages to using cloud computing in healthcare. In this blog post, we’ll explore the different types of cloud computing in healthcare, as well as the benefits and disadvantages of this technology.
Types of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
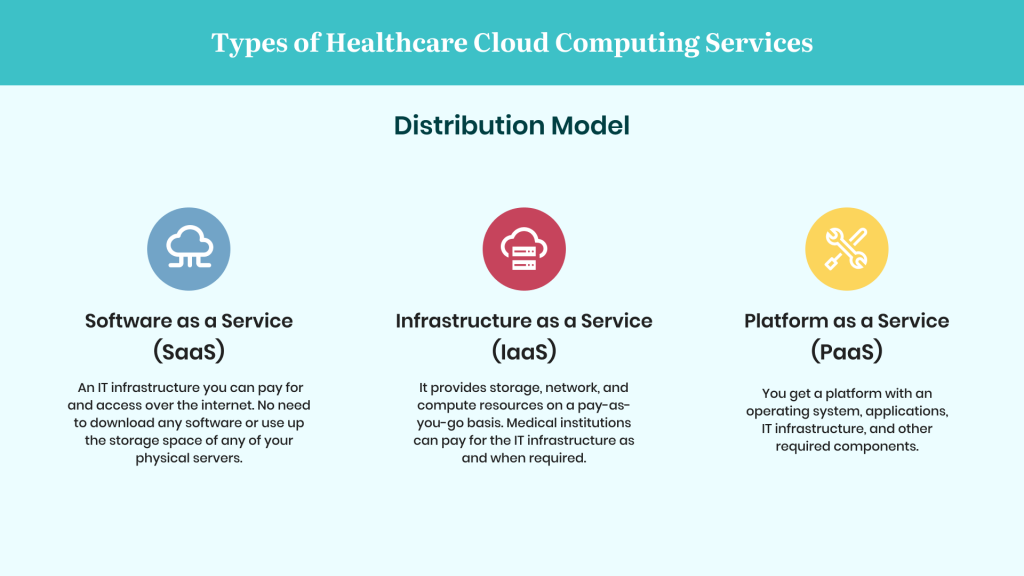
There are three main types of cloud computing in healthcare:
Software as a Service (SaaS):
SaaS is a cloud computing model where the software is hosted by a third-party provider and accessed over the internet. In healthcare, this might include electronic health record (EHR) systems, telemedicine platforms, and medical billing software.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
PaaS is a cloud computing model where a platform is provided to developers, allowing them to build and deploy applications. In healthcare, this might include software development platforms for healthcare applications.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
IaaS is a cloud computing model where infrastructure, such as servers, storage, and networking, is provided by a third-party provider. In healthcare, this might include cloud-based data storage and backup solutions.
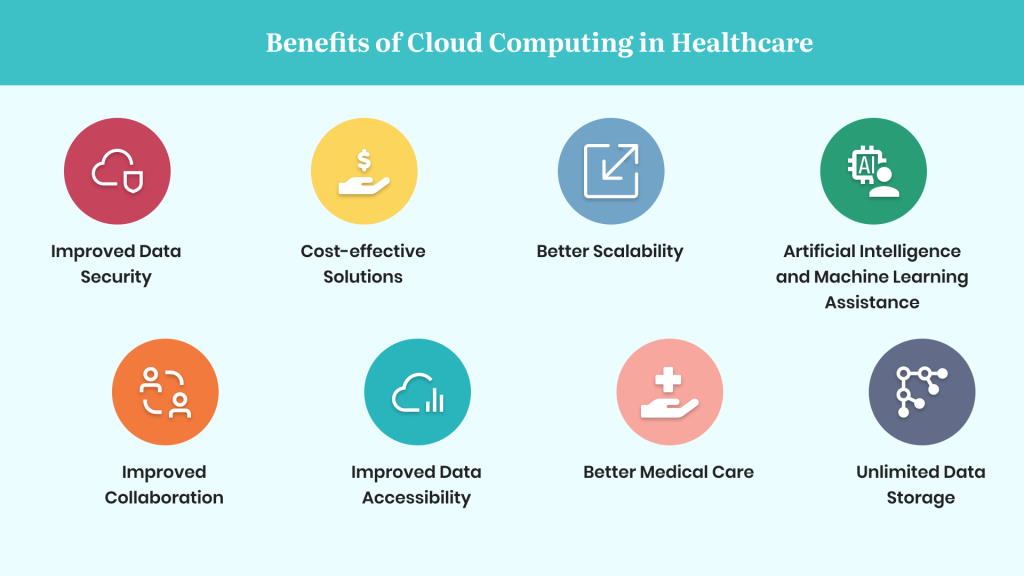
Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cost savings:
By using cloud computing, healthcare organizations can reduce the need for expensive hardware and maintenance costs. Instead, they pay a subscription fee to a cloud provider, which often works out to be more cost-effective in the long run.
Scalability:
Cloud computing allows healthcare organizations to easily scale their resources up or down as needed. This means they can quickly and easily respond to changes in demand or business needs.
Increased collaboration:
Cloud computing makes it easier for healthcare professionals to collaborate and share data securely. This is especially important for telemedicine and remote healthcare, where patients may be located in different parts of the world.
Improved security:
Cloud providers often have more robust security measures in place than healthcare organizations can implement on their own. This means that healthcare data is often more secure when stored in the cloud.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Security concerns:
While cloud providers often have more robust security measures in place, there is still a risk that healthcare data could be compromised. This risk is heightened when data is being transferred between the cloud and other devices.
Reliance on internet connectivity:
Cloud computing relies on internet connectivity, which means that healthcare organizations may experience downtime or other issues if their internet connection is disrupted.
Compliance challenges:
Healthcare organizations are subject to a range of regulations and standards, such as HIPAA and GDPR. These regulations can make it challenging for healthcare organizations to ensure compliance when using cloud computing.
Data sovereignty:
Healthcare organizations may need to ensure that their data is stored in a specific geographic location to comply with local data protection laws. This can be challenging if their cloud provider has data centers located in multiple countries.
Cloud Outage:
Healthcare services are required 24/7 in all hospitals and they cannot afford to have a lack of patient data, AI assistance, or assistance from other medical professionals at a time when it may save the lives of patients. These institutions will need a contingency plan for cloud outages since they are unavoidable.
Conclusion
healthcare organizations must ensure that their data is stored in specific geographic locations to comply with local data protection laws, which can be challenging if their cloud provider has data centers in multiple countries. Despite the challenges, the benefits of cloud computing in healthcare far outweigh the risks. As cloud computing technology continues to evolve, healthcare organizations will increasingly adopt this technology to improve their operations and provide better patient care.
Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare

